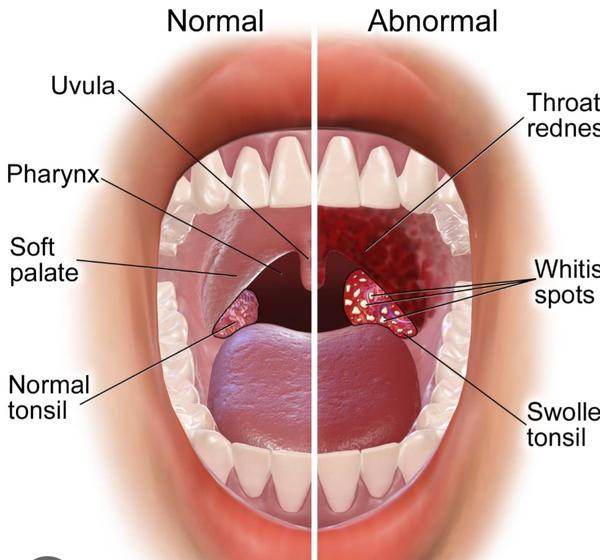
Throat infections are common and can leave you feeling miserable with symptoms like a sore throat, cough, or difficulty swallowing. But if you’ve caught one, you might be wondering, “Is this something I can spread to others?” Let’s dive into the details of throat infections, their contagiousness, and what you can do to protect yourself and others.
What Causes Throat Infections?
Throat infections are typically caused by either viruses or bacteria. Here’s a breakdown of both:
- Viral Throat Infections: Viruses are the most common culprits behind sore throats. These infections are often mild and go away on their own. Examples include:
- Common cold
- Flu (influenza)
- COVID-19
- Mononucleosis (Mono)
- Adenovirus
- Bacterial Throat Infections: While less common, bacterial infections can lead to more severe throat pain. The most notorious one is strep throat, caused by the bacteria Streptococcus pyogenes. Other bacterial infections, like those from Haemophilus influenzae, can also cause a sore throat.
So, Are Throat Infections Contagious?
Yes, both viral and bacterial throat infections can be contagious, but they spread in slightly different ways. Here’s how:
1. Viral Throat Infections:
- How it spreads: Viruses spread primarily through respiratory droplets when someone who is infected coughs, sneezes, talks, or even breathes.
- Contagious period: A viral infection can be contagious for several days, even before symptoms appear, and while symptoms are still present.
- Common viral throat infections like the common cold and flu are particularly contagious. If you’re sick with a viral infection, it’s best to stay home from school or work to avoid spreading it to others.
2. Bacterial Throat Infections (like Strep Throat):
- How it spreads: Similar to viral infections, bacterial infections spread through respiratory droplets. However, they can also spread by touching surfaces contaminated with bacteria and then touching your face, especially your mouth or nose.
- Contagious period: Bacterial infections can be contagious as long as symptoms are present and, in some cases, even up to 24 hours after starting antibiotic treatment. For example, once a person with strep throat has been on antibiotics for 24 hours, they are usually no longer contagious.
How Long Are Throat Infections Contagious?
The duration of contagiousness depends on the cause of the infection:
- Viral infections: Generally, you’re most contagious in the first 2-3 days of illness, but you may remain contagious for up to a week.
- Bacterial infections (like strep throat): You can spread the bacteria as long as you have symptoms and until antibiotics kick in—usually within 24 hours of starting treatment.
How to Prevent the Spread of Throat Infections
While it might be tough to avoid catching a throat infection, there are simple steps you can take to minimize the risk of spreading it to others:
- Wash your hands frequently – This is the most effective way to prevent the spread of infections.
- Cover your mouth when coughing or sneezing – Use a tissue, or if you don’t have one, cough or sneeze into your elbow to reduce the number of droplets in the air.
- Avoid close contact with others – Stay home if you’re sick and avoid close interactions, especially with vulnerable individuals like the elderly or those with weakened immune systems.
- Disinfect common surfaces – Bacteria and viruses can linger on surfaces like doorknobs, light switches, and phones, so wipe them down frequently, especially if you’re sick.
When Should You Seek Medical Attention?
Most throat infections can be managed at home with rest, hydration, and over-the-counter medications for pain relief. However, certain symptoms warrant a visit to your healthcare provider:
- Severe pain or difficulty swallowing
- A high fever that doesn’t go away
- A rash (could indicate conditions like scarlet fever from strep throat)
- Swollen lymph nodes or tonsils
- Persistent symptoms lasting more than a week
If a bacterial infection is suspected, your doctor may take a throat culture (or rapid strep test) to confirm the diagnosis. If it’s strep throat, a course of antibiotics is usually prescribed.
Final Thoughts
Throat infections, whether viral or bacterial, can be contagious. Practicing good hygiene, staying home when you’re sick, and following the advice of your doctor can help you manage and prevent the spread of these infections. Remember, while most throat infections aren’t severe, it’s always a good idea to monitor your symptoms and seek medical care if things don’t improve.
Stay healthy, and take care of yourself—and other
Dr. Khushboo V Sharma
BAMS,CGO
Director at Kaith Hospital